—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
News
New UK Cyber Monitoring Centre Introduces ‘Richter Scale’ for Cyber-Attacks
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Lazarus Group Targets Bitdefender Researcher with LinkedIn Recruiting Scam
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
NCSC Issues Guidance to Protect UK Research and Innovation
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Spanish Police Arrest Suspected NATO and US Army Hacker
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Sophos schließt Übernahme von Secureworks ab
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
AIs and Robots Should Sound Robotic
Most people know that robots no longer sound like tinny trash cans. They sound like Siri, Alexa, and Gemini. They sound like the voices in labyrinthine customer support phone trees. And even those robot voices are being made obsolete by new AI-generated voices that can mimic every vocal nuance and tic of human speech, down to specific regional accents. And with just a few seconds of audio, AI can now clone someone’s specific voice.
This technology will replace humans in many areas. Automated customer support will save money by cutting staffing at call centers. AI agents will make calls on our behalf, conversing with others in natural language. All of that is happening, and will be commonplace soon.
But there is something fundamentally different about talking with a bot as opposed to a person. A person can be a friend. An AI cannot be a friend, despite how people might treat it or react to it. AI is at best a tool, and at worst a means of manipulation. Humans need to know whether we’re talking with a living, breathing person or a robot with an agenda set by the person who controls it. That’s why robots should sound like robots.
You can’t just label AI-generated speech. It will come in many different forms. So we need a way to recognize AI that works no matter the modality. It needs to work for long or short snippets of audio, even just a second long. It needs to work for any language, and in any cultural context. At the same time, we shouldn’t constrain the underlying system’s sophistication or language complexity.
We have a simple proposal: all talking AIs and robots should use a ring modulator. In the mid-twentieth century, before it was easy to create actual robotic-sounding speech synthetically, ring modulators were used to make actors’ voices sound robotic. Over the last few decades, we have become accustomed to robotic voices, simply because text-to-speech systems were good enough to produce intelligible speech that was not human-like in its sound. Now we can use that same technology to make robotic speech that is indistinguishable from human sound robotic again.
A ring modulator has several advantages: It is computationally simple, can be applied in real-time, does not affect the intelligibility of the voice, and—most importantly—is universally “robotic sounding” because of its historical usage for depicting robots.
Responsible AI companies that provide voice synthesis or AI voice assistants in any form should add a ring modulator of some standard frequency (say, between 30-80 Hz) and of a minimum amplitude (say, 20 percent). That’s it. People will catch on quickly.
Here are a couple of examples you can listen to for examples of what we’re suggesting. The first clip is an AI-generated “podcast” of this article made by Google’s NotebookLM featuring two AI “hosts.” Google’s NotebookLM created the podcast script and audio given only the text of this article. The next two clips feature that same podcast with the AIs’ voices modulated more and less subtly by a ring modulator:
Raw audio sample generated by Google’s NotebookLM
Audio sample with added ring modulator (30 Hz-25%)
Audio sample with added ring modulator (30 Hz-40%)
We were able to generate the audio effect with a 50-line Python script generated by Anthropic’s Claude. One of the most well-known robot voices were those of the Daleks from Doctor Who in the 1960s. Back then robot voices were difficult to synthesize, so the audio was actually an actor’s voice run through a ring modulator. It was set to around 30 Hz, as we did in our example, with different modulation depth (amplitude) depending on how strong the robotic effect is meant to be. Our expectation is that the AI industry will test and converge on a good balance of such parameters and settings, and will use better tools than a 50-line Python script, but this highlights how simple it is to achieve.
Of course there will also be nefarious uses of AI voices. Scams that use voice cloning have been getting easier every year, but they’ve been possible for many years with the right know-how. Just like we’re learning that we can no longer trust images and videos we see because they could easily have been AI-generated, we will all soon learn that someone who sounds like a family member urgently requesting money may just be a scammer using a voice-cloning tool.
We don’t expect scammers to follow our proposal: They’ll find a way no matter what. But that’s always true of security standards, and a rising tide lifts all boats. We think the bulk of the uses will be with popular voice APIs from major companies—and everyone should know that they’re talking with a robot.
This essay was written with Barath Raghavan, and originally appeared in IEEE Spectrum.
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Experts Flag Security, Privacy Risks in DeepSeek AI App
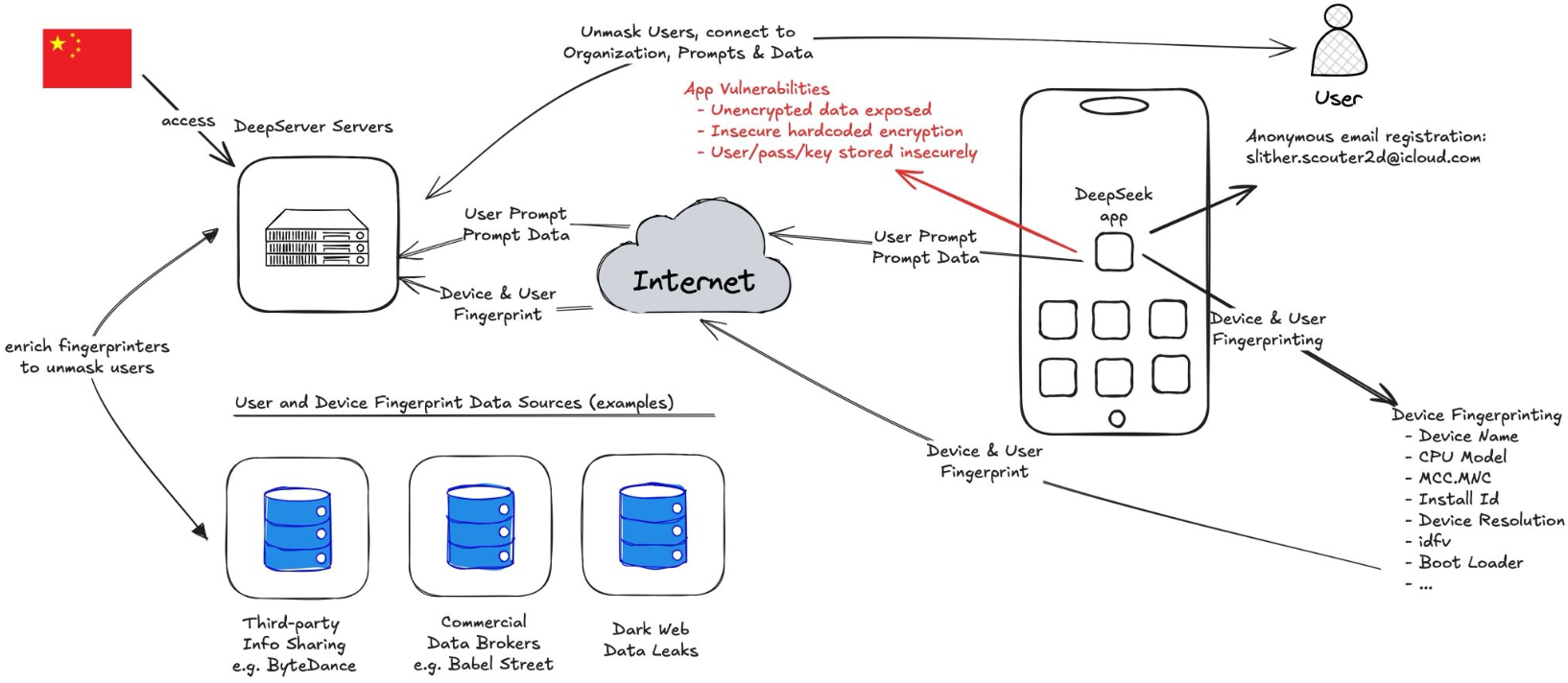
New mobile apps from the Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) company DeepSeek have remained among the top three “free” downloads for Apple and Google devices since their debut on Jan. 25, 2025. But experts caution that many of DeepSeek’s design choices — such as using hard-coded encryption keys, and sending unencrypted user and device data to Chinese companies — introduce a number of glaring security and privacy risks.

Public interest in the DeepSeek AI chat apps swelled following widespread media reports that the upstart Chinese AI firm had managed to match the abilities of cutting-edge chatbots while using a fraction of the specialized computer chips that leading AI companies rely on. As of this writing, DeepSeek is the third most-downloaded “free” app on the Apple store, and #1 on Google Play.
DeepSeek’s rapid rise caught the attention of the mobile security firm NowSecure, a Chicago-based company that helps clients screen mobile apps for security and privacy threats. In a teardown of the DeepSeek app published today, NowSecure urged organizations to remove the DeepSeek iOS mobile app from their environments, citing security concerns.
NowSecure founder Andrew Hoog said they haven’t yet concluded an in-depth analysis of the DeepSeek app for Android devices, but that there is little reason to believe its basic design would be functionally much different.
Hoog told KrebsOnSecurity there were a number of qualities about the DeepSeek iOS app that suggest the presence of deep-seated security and privacy risks. For starters, he said, the app collects an awful lot of data about the user’s device.
“They are doing some very interesting things that are on the edge of advanced device fingerprinting,” Hoog said, noting that one property of the app tracks the device’s name — which for many iOS devices defaults to the customer’s name followed by the type of iOS device.
The device information shared, combined with the user’s Internet address and data gathered from mobile advertising companies, could be used to deanonymize users of the DeepSeek iOS app, NowSecure warned. The report notes that DeepSeek communicates with Volcengine, a cloud platform developed by ByteDance (the makers of TikTok), although NowSecure said it wasn’t clear if the data is just leveraging ByteDance’s digital transformation cloud service or if the declared information share extends further between the two companies.
Perhaps more concerning, NowSecure said the iOS app transmits device information “in the clear,” without any encryption to encapsulate the data. This means the data being handled by the app could be intercepted, read, and even modified by anyone who has access to any of the networks that carry the app’s traffic.
“The DeepSeek iOS app globally disables App Transport Security (ATS) which is an iOS platform level protection that prevents sensitive data from being sent over unencrypted channels,” the report observed. “Since this protection is disabled, the app can (and does) send unencrypted data over the internet.”
Hoog said the app does selectively encrypt portions of the responses coming from DeepSeek servers. But they also found it uses an insecure and now deprecated encryption algorithm called 3DES (aka Triple DES), and that the developers had hard-coded the encryption key. That means the cryptographic key needed to decipher those data fields can be extracted from the app itself.
There were other, less alarming security and privacy issues highlighted in the report, but Hoog said he’s confident there are additional, unseen security concerns lurking within the app’s code.
“When we see people exhibit really simplistic coding errors, as you dig deeper there are usually a lot more issues,” Hoog said. “There is virtually no priority around security or privacy. Whether cultural, or mandated by China, or a witting choice, taken together they point to significant lapse in security and privacy controls, and that puts companies at risk.”
Apparently, plenty of others share this view. Axios reported on January 30 that U.S. congressional offices are being warned not to use the app.
“[T]hreat actors are already exploiting DeepSeek to deliver malicious software and infect devices,” read the notice from the chief administrative officer for the House of Representatives. “To mitigate these risks, the House has taken security measures to restrict DeepSeek’s functionality on all House-issued devices.”
TechCrunch reports that Italy and Taiwan have already moved to ban DeepSeek over security concerns. Bloomberg writes that The Pentagon has blocked access to DeepSeek. CNBC says NASA also banned employees from using the service, as did the U.S. Navy.
Beyond security concerns tied to the DeepSeek iOS app, there are indications the Chinese AI company may be playing fast and loose with the data that it collects from and about users. On January 29, researchers at Wiz said they discovered a publicly accessible database linked to DeepSeek that exposed “a significant volume of chat history, backend data and sensitive information, including log streams, API secrets, and operational details.”
“More critically, the exposure allowed for full database control and potential privilege escalation within the DeepSeek environment, without any authentication or defense mechanism to the outside world,” Wiz wrote. [Full disclosure: Wiz is currently an advertiser on this website.]
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment on the report from DeepSeek and from Apple. This story will be updated with any substantive replies.
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Sophisticated Phishing Campaign Targets Ukraine’s Largest Bank
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains
Ransomware Payments Decline 35% as Victims Resist Demands
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains