In January 2022, KrebsOnSecurity identified a Russian man named Mikhail Matveev as “Wazawaka,” a cybercriminal who was deeply involved in the formation and operation of multiple ransomware groups. The U.S. government indicted Matveev as a top ransomware purveyor a year later, offering $10 million for information leading to his arrest. Last week, the Russian government reportedly arrested Matveev and charged him with creating malware used to extort companies.

An FBI wanted poster for Matveev.
Matveev, a.k.a. “Wazawaka” and “Boriselcin” worked with at least three different ransomware gangs that extorted hundreds of millions of dollars from companies, schools, hospitals and government agencies, U.S. prosecutors allege.
Russia’s interior ministry last week issued a statement saying a 32-year-old hacker had been charged with violating domestic laws against the creation and use of malicious software. The announcement didn’t name the accused, but the Russian state news agency RIA Novosti cited anonymous sources saying the man detained is Matveev.
Matveev did not respond to requests for comment. Daryna Antoniuk at TheRecord reports that a security researcher said on Sunday they had contacted Wazawaka, who confirmed being charged and said he’d paid two fines, had his cryptocurrency confiscated, and is currently out on bail pending trial.
Matveev’s hacker identities were remarkably open and talkative on numerous cybercrime forums. Shortly after being identified as Wazawaka by KrebsOnSecurity in 2022, Matveev published multiple selfie videos on Twitter/X where he acknowledged using the Wazawaka moniker and mentioned several security researchers by name (including this author). More recently, Matveev’s X profile (@ransomboris) posted a picture of a t-shirt that features the U.S. government’s “Wanted” poster for him.
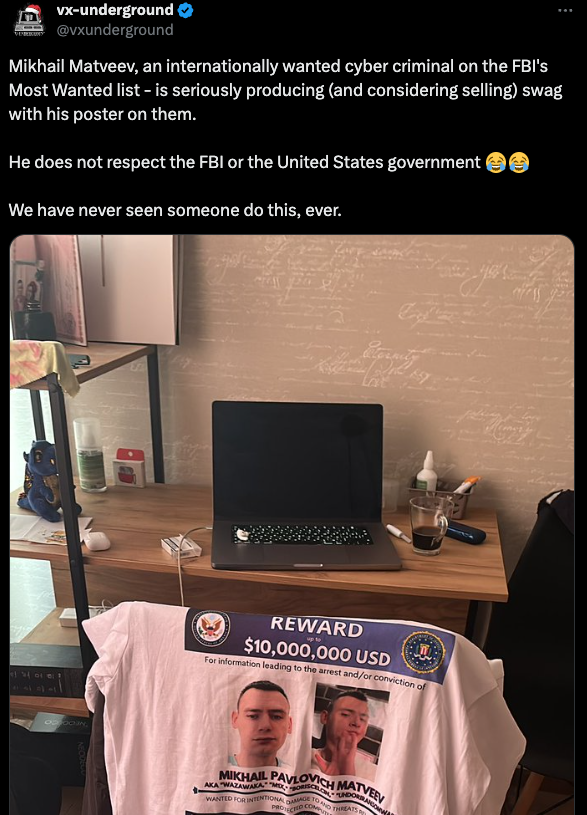
An image tweeted by Matveev showing the Justice Department’s wanted poster for him on a t-shirt. image: x.com/vxunderground
The golden rule of cybercrime in Russia has always been that as long as you never hack, extort or steal from Russian citizens or companies, you have little to fear of arrest. Wazawaka claimed he zealously adhered to this rule as a personal and professional mantra.
“Don’t shit where you live, travel local, and don’t go abroad,” Wazawaka wrote in January 2021 on the Russian-language cybercrime forum Exploit. “Mother Russia will help you. Love your country, and you will always get away with everything.”
Still, Wazawaka may not have always stuck to that rule. At several points throughout his career, Wazawaka claimed he made good money stealing accounts from drug dealers on darknet narcotics bazaars.
Cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 said Matveev’s arrest raises more questions than answers, and that Russia’s motivation here likely goes beyond what’s happening on the surface.
“It’s possible this is a shakedown by Kaliningrad authorities of a local internet thug who has tens of millions of dollars in cryptocurrency,” Intel 471 wrote in an analysis published Dec. 2. “The country’s ingrained, institutional corruption dictates that if dues aren’t paid, trouble will come knocking. But it’s usually a problem money can fix.
Intel 471 says while Russia’s court system is opaque, Matveev will likely be open about the proceedings, particularly if he pays a toll and is granted passage to continue his destructive actions.
“Unfortunately, none of this would mark meaningful progress against ransomware,” they concluded.
Although Russia traditionally hasn’t put a lot of effort into going after cybercriminals within its borders, it has brought a series of charges against alleged ransomware actors this year. In January, four men tied to the REvil ransomware group were sentenced to lengthy prison terms. The men were among 14 suspected REvil members rounded up by Russia in the weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022.
Earlier this year, Russian authorities arrested at least two men for allegedly operating the short-lived Sugarlocker ransomware program in 2021. Aleksandr Ermakov and Mikhail Shefel (now legally Mikhail Lenin) ran a security consulting business called Shtazi-IT. Shortly before his arrest, Ermakov became the first ever cybercriminal sanctioned by Australia, which alleged he stole and leaked data on nearly 10 million customers of the Australian health giant Medibank.
In December 2023, KrebsOnSecurity identified Lenin as “Rescator,” the nickname used by the cybercriminal responsible for selling more than 100 million payment cards stolen from customers of Target and Home Depot in 2013 and 2014. Last month, Shefel admitted in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity that he was Rescator, and claimed his arrest in the Sugarlocker case was payback for reporting the son of his former boss to the police.
Ermakov was sentenced to two years probation. But on the same day my interview with Lenin was published here, a Moscow court declared him insane, and ordered him to undergo compulsory medical treatment, The Record’s Antoniuk notes.
—————
Free Secure Email – Transcom Sigma
Boost Inflight Internet
Transcom Hosting
Transcom Premium Domains